A battery’s charge and discharge rates are controlled by battery C Rates. The battery C Rating is the measurement of current in which a battery is charged and discharged at. The capacity of a battery is generally rated and labelled at the 1C Rate (1C current), this means a fully charged battery with a capacity of 10Ah should be able to provide 10 Amps for one hour. That same 10Ah battery being discharged at a C Rating of 0.5C will provide 5 Amps over two hours, and if discharged at a 2C Rate it will provide 20 Amps for 30 minutes. The C Rating of a battery is important to know as with the majority of batteries the available stored energy depends on the speed of the charge and discharge currents.
BATTERY C RATE CHART
The below chart shows the different battery C Rates along with their service times. It is important to know that even though discharging a battery at different C Rates should use the same calculations as an identical amount of energy, in reality there are likely to be some internal energy losses. At higher C Rates some of the energy can be lost and turned in to heat which can result in lowering the capacity by 5% or more.
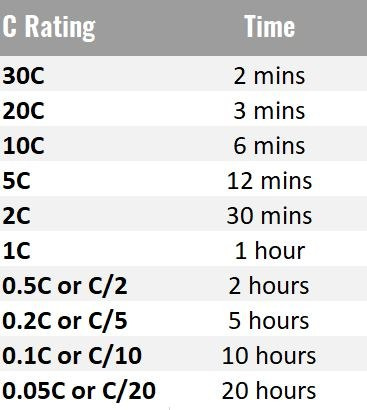
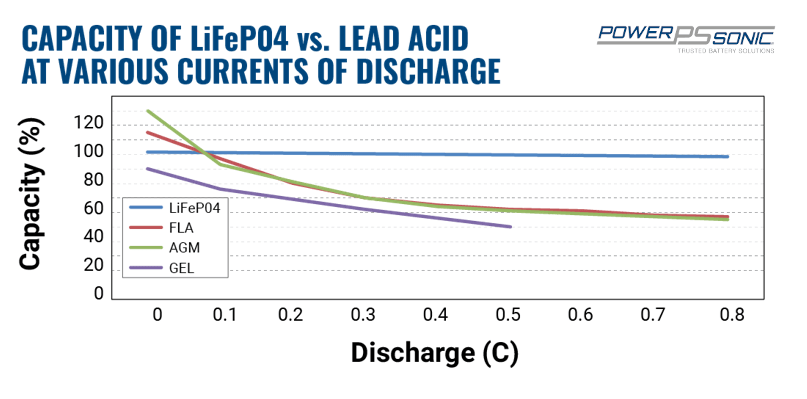
To obtain a reasonably good capacity reading, manufacturers commonly rate alkaline and lead acid batteries at a very low 0.05C, or a 20-hour discharge. Even at this slow discharge rate, lead acid seldom attains a 100 percent capacity as the batteries are overrated. Manufacturers provide capacity offsets to adjust for the discrepancies if discharged at a higher C rate than specified.
HOW TO CALCULATE C RATING OF A BATTERY
A battery’s C Rating is defined by the rate of time in which it takes to charge or discharge. You can increase or decrease the C Rate and as a result this will affect the time it takes the battery to charge or discharge. The C Rate charge or discharge time changes in relation to the rating. 1C is equal to 60 minutes, 0.5C to 120 minutes and a 2C rating is equal to 30 minutes.
The formula is simple.
t = Time Cr = C Rate t = 1 / Cr (to view in hours) t = 60 minutes / Cr (to view in minutes)
0.5C Rate Example
- 2300mAh Battery
- 2300mAh / 1000 = 2.3Ah
- 0.5C x 2.3Ah = 1.15 Amps available
- 1 / 0.5C = 2 hours
- 60 / 0.5C = 120 minutes
2C Rate Example
- 2300mAh Battery
- 2300mAh / 1000 = 2.3Ah
- 2C x 2.3Ah = 4.6 Amps available
- 1 / 2C = 0.5 hours
- 60 / 2C = 30 minutes
30C Rate Example
- 2300mAh Battery
- 2300mAh / 1000 = 2.3Ah
- 30C x 2.3Ah = 69 Amps available
- 60 / 30C = 2 minutes
You can see the 30C rate example on the datasheet for Power Sonic 26650 LiFePO4 power cell
You can use the formula below to calculate a battery’s output current, power, and energy based on its C rating.
Er = Rated energy (Ah) Cr = C Rate I = Current of charge or discharge (Amps) I = Cr * Er Cr = I / Er
HOW TO FIND C RATING OF A BATTERY
Smaller batteries are commonly rated at the 1C rating, which is also known as the one-hour rate. For example, if your battery is labeled 3000mAh at the one-hour rate, then the 1C rating is 3000mAh. You will generally find the C rate of your battery on its label and the battery data sheet. Different battery chemistries will sometimes display different C rates; for instance, lead acid batteries are generally rated at a very low discharge rate, often a 0.05C or 20-hour rate. The chemistry and design of your battery will determine the maximum C rate of your battery. Lithium batteries, for instance, can tolerate much higher discharging C Rates than other chemistries such as alkaline. If you cannot find the battery C rating on the label or datasheet we advise contacting the battery manufacturer directly.
APPLICATIONS REQUIRING HIGH C RATES
There are an increasing number of applications and devices on the market that require a high C Rate battery. These include industrial and consumer applications like RC models, drones, robotics, and vehicle jump starters. All these applications require a powerful energy burst in a short period of time.

Most jump starters can require up to 80C Rate discharge and in the RC industry there are high-rate discharge batteries used up to 50C Rate! There are some batteries on the market that claim even higher C Rates based on maximum pulse discharge rates, which require the battery to reach full discharge in just a few seconds. However most applications, do not need such high C Rates.
If you need any help finding the right battery for your application, please get in touch with one of the Power-Sonic application engineers.






