The EV market is booming, with new models of electric vehicles becoming available all the time. From hot hatchbacks and coupes to SUVs and pickup trucks. But what is the difference between the types of electric vehicles and cars available? Some electric vehicles run solely on battery power; others, known as hybrids, combine an electric motor with an internal combustion engine in various ways. Then, there are fuel cell electric vehicles and even solar electric cars. This guide to the different types of electric vehicles will provide an overview of the types of EVs and how they work.
BATTERY ELECTRIC VEHICLES (BEVs)
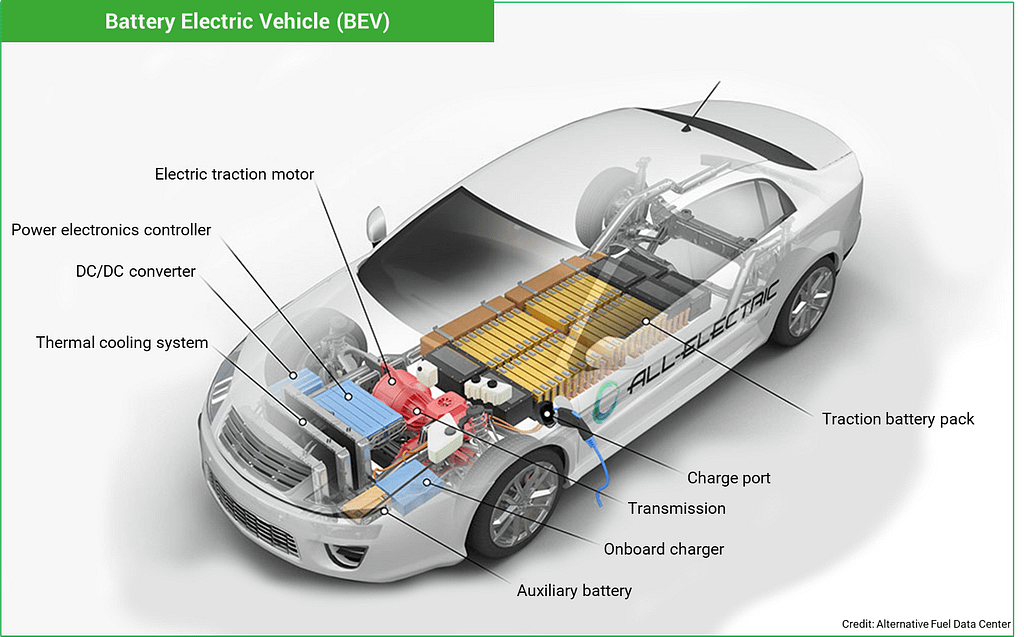
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), also referred to as ‘all-electric vehicles’ or ‘pure electric vehicles,’ run entirely on electricity only and have no gasoline engine. BEVs are moved by one or more electric motors powered by rechargeable batteries. Most of today’s BEVs have lithium batteries. Auto manufacturers choose lithium due to their high power-to-weight ratio resulting in a more extended range in a smaller physical footprint. The battery packs are charged using electricity delivered through an EV charger. There are different types or ‘levels’ of EV chargers, with level 1 being the slowest and level 3 being the fastest; most BEVs can fast charge via a level 3 charger.
Unlike gasoline-powered vehicles, BEVs are zero-emission vehicles that do not produce any harmful emissions or air pollution. Today’s BEVs have a driving range-per-charge of between 50 to 350 miles; although new models with longer ranges are being released, the 2022 Lucid Air Dream Edition boasts over 500 miles.
EXAMPLES OF AVAILABLE BATTERY ELECTRIC VEHICLES (BEVs)
Audi e-tron, Audi e-tron GT, Audi e-tron Sportback, BMW i3, BMW i4, Chevrolet Bolt EV, Chevrolet Bolt EUV, Ford Mustang Mach-e, GMC Hummer EV, Hyundai Ioniq Electric, Hyundai KONA Electric, Jaguar I-Pace, Kia EV6, Kia Niro EV, Lucid Air Dream Edition, Mazda MX-30, Mercedes EQS, MG5 EV, Mini Cooper Electric, Mini Cooper SE Electric, Nissan LEAF, Nissan LEAF Plus, Peugeot e-208, Polestar 2, Porsche Taycan 4S, Porsche Taycan Cross Turismo, Rivian R1S, Rivian R1T, Skoda ENYAQ iV, Tesla Model X, Tesla Model Y, Tesla Model S, Tesla Model 3, Tesla Model S Plaid, Volkswagen ID.4, Volvo C40 Recharge, Volvo XC40 Recharge.
PLUG-IN HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLES (PHEVs)
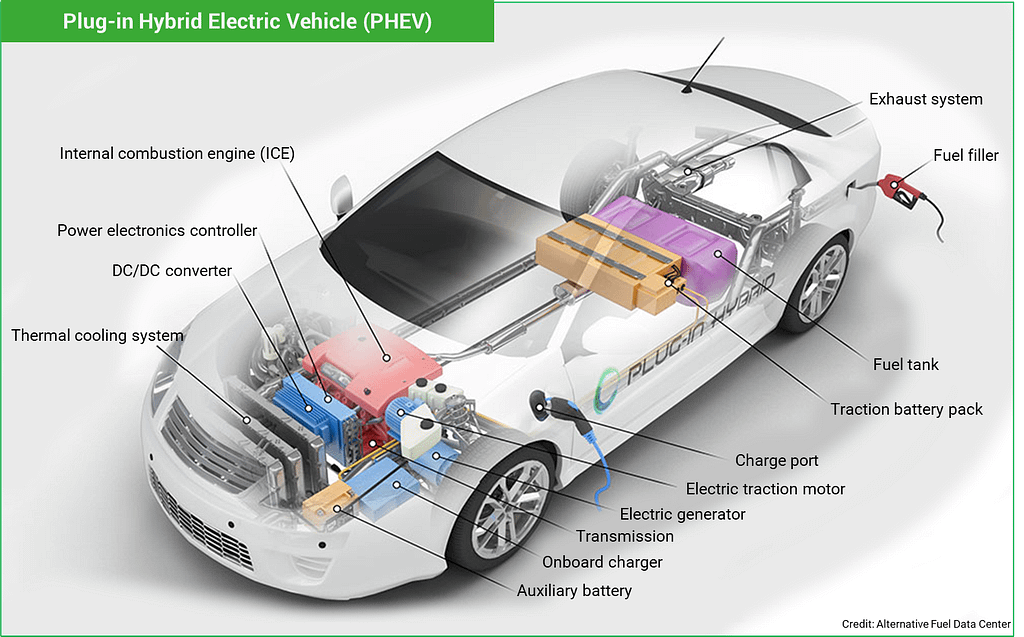
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) use batteries to power an electric motor and incorporate an internal combustion engine (ICE) that can recharge the batteries to enable longer driving ranges. A PHEV typically runs on electricity stored in the battery until nearly depleted, generally around 10 – 50 miles depending on the vehicle model and battery size. Then the car automatically switches over to use the ICE and can travel several hundred miles on a tank of fuel. This can dramatically reduce fuel use and emissions, especially on short journeys. When no electricity is available, a Plug-in Hybrid can run on fuel alone. All PHEV batteries can be charged by a Level 1 or a Level 2 type EV charger, but most cannot be charged by a level 3 DC fast charger.
EXAMPLES OF AVAILABLE PLUG-IN HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLES (PHEVs)
Audi A3 E-Tron, Audi Q5 TFSIe PHEV, Audi A7 TFSIe, Bentley Bentagya, BMW 225xe, BMW 330e, BMWi8, BMWx5 xdrive40e, Chevy Volt, Chrysler Pacifica, Fiat 500e, Ford C-Max Energi, Ferrari SF90 Stradale, Ford Escape PHEV, Ford Fusion Energi, Hyundai IONIQ PHEV, Hyundai Sonata, Jeep Wrangler 4xe, Karma Revero GT, Kia Optima, Land Rover Defender PHEV, Land Rover Range Rover PHEV, Lincoln Aviator Grand Touring, Mercedes C300e, Mercedes C530e, Mercedes E350e SE, Mercedes GLE550e, Mercedes S550e, Mini Cooper SE Countryman, Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV, Porsche Cayenne S E-Hybrid, Porsche Panamera S E-Hybrid, Skoda Octavia iV, Subaru Crosstrek PHEV, Toyota Prius, Toyota RAV4, Volkswagen Golf GTE, Volkswagen Passat GTE, Volvo XC90 TB, Volvo XC60 T8 PHEV.
HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLES (HEVs)
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs), sometimes referred to as ‘self-charging hybrids,’ use both an internal combustion engine and an electric motor, which uses electricity stored in a battery pack. The main difference between a PHEV and an HEV is that you cannot plug an HEV into an EV charger to charge the battery. Instead, the onboard battery pack is charged via the engine and regenerative braking. The additional power generated by the electric motor may allow for the vehicle to have a smaller engine. The battery pack can work as an auxiliary battery for the car, helping to reduce idling when stopped; this results in better fuel economy and lower emissions when compared to a conventional engine car. Toyota was one of the pioneers in introducing and popularizing Hybrid Electric Vehicles with the Toyota Prius.
There are different types of HEVS, they include:
- Mild Hybrid Electric Vehicles (MHEVs) – Also referred to as ‘Micro Hybrids,’ ‘Power Assist Hybrids’ and ‘Battery Assisted Hybrid Electric Vehicles (BAHVs).’ It uses the battery pack and electric motor to help power the vehicle and enables the engine to be shut off when the car has stopped. MHEVs cannot drive the vehicle on electricity alone and are not as fuel-efficient as a full hybrid.
- Full Hybrid Electric Vehicles (FHEVs) – Full hybrids have larger capacity battery packs and more powerful electric motors than mild hybrids and can travel short distances at low speeds on battery power.

EXAMPLES OF AVAILABLE HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLES (HEVs)
Audi A8 Le-tron, Audi Q7 SUV, Buick LaCrosse, Dodge Ram 1500 eTorque, Ford Focus MHEV, Ford Mondeo Hybrid, Honda CR-Z, Honda Insight, Hyundai IONIQ HYBRID, Hyundai Tucson 48V, Kia Niro Hybrid, Land Rover Discovery Sport MHEV, Lexus CT200h, Mercedes-Benz S 400 HYBRID, Range Rover Evoque, Renault Clio E-Tech, Silverado 1500, Suzuki Swift SHVS, Toyota Prius, Toyota Yaris Hybrid.
HOW DO HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLES WORK?
There are different ways that a hybrid can combine the power from an electric motor and the internal combustion engine. The most common type is a ‘Parallel Hybrid’ that connects the engine and the electric motor to the wheels through mechanical coupling. In this scenario, the electric motor and the engine can drive the wheels directly.
‘Series Hybrids’ only use the electric motor to drive the wheels and can often be referred to as Extended-Range Electric Vehicles (EREVs) or Range-Extended Electric Vehicles (REEVs).
There is also ‘Series-Parallel Hybrids’ where the vehicle can be powered by the engine working alone, the electric motor on its own, or by both working together; this is designed so that the engine can run at its optimum range as often as possible. Below, we illustrate how mechanical and electric power is delivered in hybrid cars.

FUEL CELL ELECTRIC VEHICLES (FCEVs)
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs) create zero tailpipe emissions powered by hydrogen. An FCEV uses a similar system as a Battery Electric Vehicle to run the vehicle. In the case of an FCEV, the energy is stored as hydrogen and then converted into electricity by the fuel cell to propel the vehicle. Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles have a gas tank used to store the pure hydrogen; the tank can be fuelled up in just a few minutes, similar to how conventional ICE vehicles are filled up today.
FCEVs can reach around 300 miles on one tank of pure hydrogen. They also utilize regenerative braking technology and capture energy lost during braking, which is stored in a battery pack. There are a limited number of production FCEVs available to the public, and as of today, the refuelling infrastructure isn’t anywhere near where it needs to be to support a mass rollout of FCEVs.

EXAMPLES OF FUEL CELL ELECTRIC VEHICLES (FCEVs)
BMW iX5, Honda Clarity, Hyundai Nexo, Hyundai Nexo Blue, Hyundai Staria Fuel Cell, Ineos Grenadier Hydrogen, Kia FK, Land Rover Defender Fuel Cell, Range Rover FCEV, Toyota Mirai LE, Toyota Mirai Limited, Toyota Mirai XLE.
SOLAR ELECTRIC VEHICLES (SEVs)
Solar Electric Vehicles (SEVs) are electric cars that use photovoltaic cells, like those used in solar panels, to convert energy generated from sunlight into electricity. The solar energy generated from the sun is used to top up the battery pack allowing for a longer range of travel when compared to a standard BEV. The generated solar energy is completely free and has no cost impact on the vehicle owner, potentially reducing the total cost of ownership of a Solar Electric Vehicle. However, you need the sun; if the sun is not out, then your SEV will act as an all-electric vehicle. SEVs can be charged using a level 1, level 2, or level 3 type EV charger. Some examples of companies that manufacture SEVs include Aptera, Lightyear, and Sono Motors.







